Arctic Wolf
| Arctic Wolf | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Canis |
| Species: | C. lupus |
| Subspecies: | C. l. arctos |
| Trinomial name | |
| Canis lupus arctos Pocock, 1935 |
|
 |
|
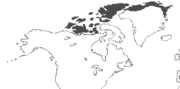
| Arctic Wolf ranges | |
The Arctic Wolf (Canis lupus arctos), also called Polar Wolf or White Wolf, is a species of mammal of the family Canidae, and a subspecies of the Gray Wolf. Arctic Wolves inhabit the Canadian Arctic, Alaska and the northern parts of Greenland.
Contents |
Anatomy
See also: Gray Wolf behavior and physiology
Though the same species as a Gray Wolf, Arctic Wolves generally are smaller than the "Forest Gray Wolves" (Arctic Wolves are sometimes called "Tundra Wolves"), being about 0.9 to 1.8 m (35 to 71 in) long including the tail, with the head and body measuring between 1 to 1.5 m (39 to 59 in);[1][2][3] males are larger than females and are more aggressive. Their shoulder heights vary from 0.63 to 0.79 m (25 to 31 in), shorter than other wolf subspecies of similar mass, their ears are smaller to trap body heat and their muzzles are much shorter.[1][2] The males weigh between 34 to 46 kg (75 to 100 lb) and females between 36 to 38 kg (79 to 84 lb) but may fall in the 45 to 70 kg (99 to 150 lb) range.[1][4] Arctic Wolves are smaller than other wolves and have long, thick white fur. Like other wolves, they have strong jaws with sharp teeth, including long canine teeth which tear flesh. During the winter, the Arctic Wolf grows a second layer of fur for protection during the harsh conditions that may occur during the season. Wolves have very good eyesight, acute hearing, and a keen sense of smell which help them hunt.
Habitat and distribution
The Arctic Wolf inhabits the northern part of Greenland, the Canadian Arctic and parts of Alaska. They have lived in North America for more than two million years. When they find a den, they make a couple of chambers for food and young. Arctic wolves live on the islands of the Canadian Arctic, and the north coast of Greenland, roughly north of 70° North latitude. The Arctic Wolf is the only subspecies of the Gray Wolf that still can be found over the whole of its original range, largely because, in their natural habitat, they rarely encounter humans.
Their habitat is extremely harsh and remote, and few scientists venture into that world during the long, dark winter – even the vast majority of Inuit live further south than the Arctic wolf. As a result, the details of their lives through much of the year are virtually unknown.
Behavior
The Arctic Wolf is one of the few mammals that can withstand the arctic weather. It can survive in sub-zero temperatures for years, in absolute darkness for five months per year, and without food for weeks. Arctic Wolves usually travel in packs of 2 to 20. They live in small family groups: a breeding pair (alpha male and female) and their cubs. The pack works together to feed and care for their cubs. Lone Arctic Wolves are young males that have left their pack to seek their own territories. They avoid other wolves, unless they are able to mate. Having found an abandoned territory, a lone Arctic Wolf will claim it by marking the territory with its scent, then gather other lone wolves into its pack. When the female is pregnant, she leaves the pack to dig a den to raise her pups. If the ice is too thick, she will move to a den or cave.
Hunting
Like all wolves, Arctic Wolves hunt in packs, preying mainly on Caribou and Muskoxen, but also Arctic Hares, seals, ptarmigan and lemmings, and smaller animals such as waterfowl.[5] To eat rodents they must pick up their scent and find the entrance to their tiny dens to flush them out. Wolves almost never attack humans. Due to the scarcity of prey, they roam large areas, up to 2,600 km2 (1,000 sq mi), and follow migrating caribou south during the winter. They are not fast runners, instead relying on stamina to take down prey.[6]
They kill their prey with a bite on the neck. Adult wolves have 42 teeth, their main weapon in hunting. They swallow food in large chunks, barely chewing it. They eat all of their prey, including the bones. Wolves can eat up to 20 pounds (9 kg) of meat at one meal. When they return from the hunt, wolves regurgitate some of the food for the hungry pups.[7]
Reproduction
Due to the Arctic's permafrost soil and the difficulty it poses for digging dens, Arctic Wolves often use rock outcroppings, caves or even shallow depressions as dens instead. After gestation of about 63 days to 75 days, birth is in late May to early June, about a month later than Gray Wolves. The mother gives birth to 2 or 3 pups, though there may be as many as 12. This is fewer pups than Gray Wolves, which have four to five. It is generally thought that the lower number is due to the scarcity of prey in the Arctic. Pups are born blind and deaf, and weigh about one pound. They are dependent on their mother for food and protection. When they are three weeks old, they are allowed outside the den. Other wolves in the pack may take care of the mother’s pups until she returns with food.[8]
References
- L. David Mech (text), Jim Brandenburg (photos), At home with the Arctic wolf, National Geographic Vol. 171 No. 5 (May 1987), pp. 562–593
- L. David Mech, The Arctic wolf: 10 years with the pack, Voyageur Press 1997, ISBN 0-89658-353-8
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 White wolf of the North
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 The Arctic Wolf
- ↑ Young Peoples Trust for the Environment
- ↑ Arctic Wolf at the Toronto Zoo
- ↑ Morelle, Rebecca (2009-01-31). "Elusive wolves caught on camera". BBC. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/7213731.stm. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ Wolf traits
- ↑ Arctic Wolf
- ↑ Wolf facts